As we discussed briefly in an earlier post, Understanding Whiplash, whiplash injuries can manifest in a wide variety of ways, including neck pain, headaches, fatigue, upper back and shoulder pain, cognitive changes and low back pain.
Due to the fact that numerous factors play into the overall whiplash trauma, such as direction of impact, speed of the vehicles involved, size of the vehicles involved, as well as sex, age and physical condition, it is impossible to predict the pattern of symptoms that each individual will suffer.
Additionally, whiplash symptoms commonly have a delayed onset, often taking weeks or months to present. There are, however, a number of conditions that are very common among those who have suffered from whiplash trauma. Below, you will learn the most common injuries from whiplash trauma. . .
Neck Pain
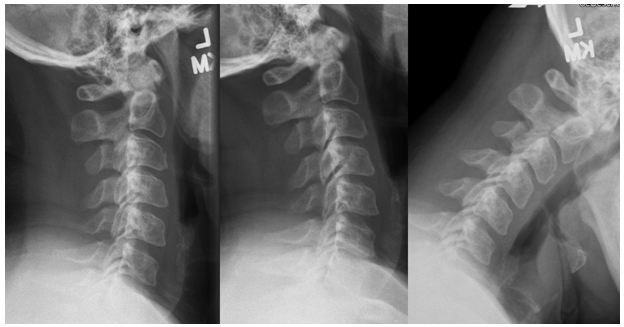
 Neck pain is the single most common complaint in whiplash trauma, being reported by over 90% of patients. Often this pain radiates across the shoulders, up into the head, and down between the shoulder blades. Whiplash injuries tend to affect all of the tissues in the neck, including the facet joints
Neck pain is the single most common complaint in whiplash trauma, being reported by over 90% of patients. Often this pain radiates across the shoulders, up into the head, and down between the shoulder blades. Whiplash injuries tend to affect all of the tissues in the neck, including the facet joints
and discs between the vertebrae, as well as all of the muscles, ligaments and nerves. Facet joint pain is the most common cause of neck pain following a car accident. Facet joint pain is usually felt on the
back of the neck, just to the right or left of center, and is usually tender to the touch. Facet joint pain cannot be visualized on x-rays or MRIs. It can only be diagnosed by physical palpation of the area.
Disc injury is also a common cause of neck pain; especially chronic pain. The outer wall of the disc (called the annulus) is made up of bundles of fibers that can be torn during a whiplash trauma. These tears, then, can lead to disc degeneration or herniation, resulting in irritation or compression of the
nerves running through the area. This compression or irritation commonly leads to radiating pain into the arms, shoulders and upper back, and may result in muscle weakness. Damage to the muscles and ligaments in the neck and upper back are the major cause of the pain experienced in the first few weeks following a whiplash injury, and is the main reason why you experience stiffness and restricted range of motion. But as the muscles have a chance to heal, they typically don’t cause as much actual pain as they contribute to abnormal movement. Damage to the ligaments often results in abnormal movement and instability.
Headaches
 After neck pain, headaches are the most prevalent complaint among those suffering from whiplash injury, affecting more than 50% of all people. While some headaches are actually the result of direct brain injury, most are related to injury of the muscles. ligaments and facet joints of the cervical spine, which refer pain to the head. Because of this, it is important to treat the supporting structures of your neck in order to help alleviate your headaches.
After neck pain, headaches are the most prevalent complaint among those suffering from whiplash injury, affecting more than 50% of all people. While some headaches are actually the result of direct brain injury, most are related to injury of the muscles. ligaments and facet joints of the cervical spine, which refer pain to the head. Because of this, it is important to treat the supporting structures of your neck in order to help alleviate your headaches.
TMJ Problems
A less common, but very debilitating disorder that results from whiplash is temporomandibular joint dysfunction (TMJ). TMJ usually begins as pain, clicking and popping noises in the jaw during movement. If not properly evaluated and treated, TMJ problems can continue to worsen and lead to headaches, facial pain, ear pain and difficulty chewing. Chiropractors have been specially trained to treat TMJ problems and often begin treatment for this on a patient’s first visit.
Brain Injury
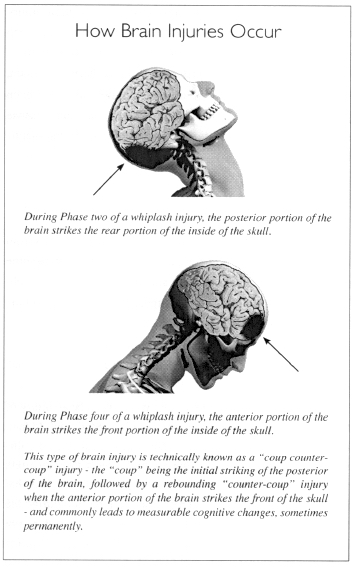 Believe it or not, mild to moderate brain injury is common following a whiplash injury, due to the forces on the brain during the four phases mentioned earlier. The human brain is a very soft structure, suspended in a watery fluid called cerebrospinal fluid. When the brain is forced forward and backward in the skull, the brain bounces off the inside of the skull, leading to bruising or bleeding in the brain itself. In some cases. patients temporarily lose consciousness and have symptoms of a mild concussion. More often, there is no loss of consciousness. but patients complain of mild confusion or disorientation just after the crash. The long-term consequences of a mild brain injury can include mild confusion, difficulty concentrating; sleep disturbances, irritability, and forgetfulness. loss of sex drive, depression and emotional instability. Although less common, the nerves responsible for your sense of smell, taste and even your vision may be affected as well, resulting in a muted sense of taste, changes in your sensation of smell and visual disturbances.
Believe it or not, mild to moderate brain injury is common following a whiplash injury, due to the forces on the brain during the four phases mentioned earlier. The human brain is a very soft structure, suspended in a watery fluid called cerebrospinal fluid. When the brain is forced forward and backward in the skull, the brain bounces off the inside of the skull, leading to bruising or bleeding in the brain itself. In some cases. patients temporarily lose consciousness and have symptoms of a mild concussion. More often, there is no loss of consciousness. but patients complain of mild confusion or disorientation just after the crash. The long-term consequences of a mild brain injury can include mild confusion, difficulty concentrating; sleep disturbances, irritability, and forgetfulness. loss of sex drive, depression and emotional instability. Although less common, the nerves responsible for your sense of smell, taste and even your vision may be affected as well, resulting in a muted sense of taste, changes in your sensation of smell and visual disturbances.
Dizziness
Dizziness following a whiplash injury usually results from injury to the facet joints of the cervical spine, although in some cases injury to the brain or brain stem may be a factor as well. Typically, this dizziness is very temporary and improves significantly with chiropractic treatment.
Low Back Pain
Although most people consider whiplash to be an injury of the neck, the low back is also commonly injured as well. In fact, low back pain is found in more than half of rear impact-collisions in which injury was reported, and almost three-quarters of all side-impact crashes. This is mostly due to the fact that the low back experiences a tremendous compression during the first two phases of a whiplash injury, even though it does not have the degree of flexion-extension injury experienced in the neck.